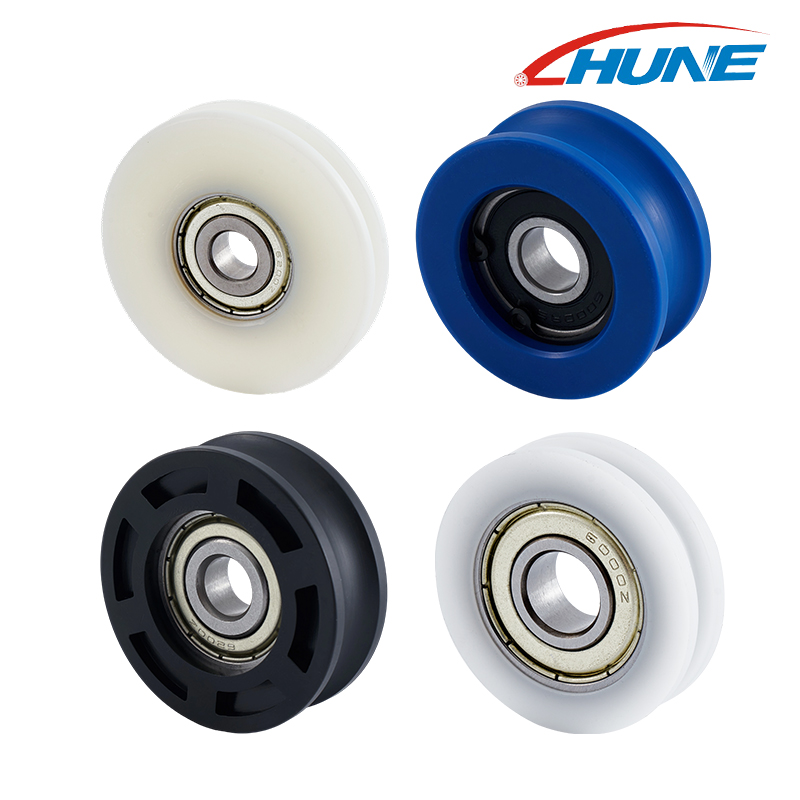
Plastic bearing pulleys are essential components in various mechanical systems, from conveyor belts and 3D printers to medical devices and home appliances. Their lightweight structure, corrosion resistance, and lower cost compared to metal alternatives make them an increasingly popular choice in modern engineering. But not all plastics are created equal. Different types of plastic materials are selected based on their mechanical strength, thermal resistance, wear properties, and application-specific needs.
Here’s a closer look at the most commonly used plastic materials in bearing pulleys and why they are preferred:
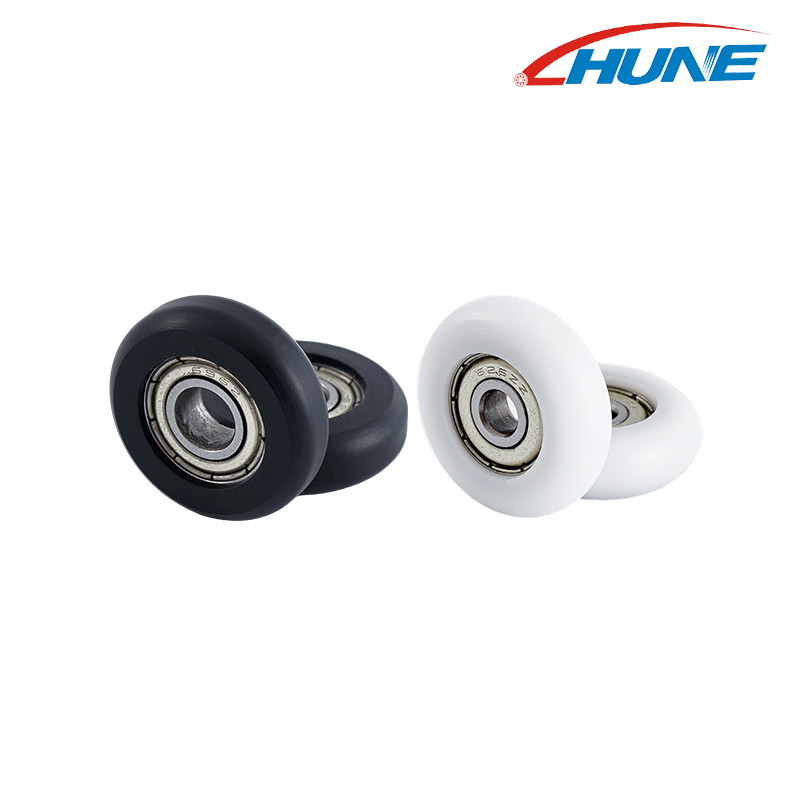

1. Nylon (Polyamide - PA)
Why it’s used:
Nylon is one of the most widely used materials for plastic bearing pulleys due to its excellent wear resistance, low friction coefficient, and high mechanical strength. It also has good fatigue resistance and performs well in moderately high-load applications.
Advantages:
High durability and tensile strength
Good resistance to abrasion
Low noise operation
Self-lubricating properties in some formulations
Limitations:
Can absorb moisture, which may affect dimensional stability
Limited performance in very high temperatures
2. Polyoxymethylene (POM or Acetal)
Why it’s used:
POM is a popular choice when precision, stiffness, and dimensional stability are required. Its low friction characteristics make it ideal for high-speed, low-load applications where smooth movement is critical.
Advantages:
Excellent dimensional stability
Low friction and high wear resistance
Minimal moisture absorption
Good chemical resistance
Limitations:
More brittle than nylon
Less impact-resistant in cold environments
3. Polyethylene (PE)
Why it’s used:
For low-cost and light-load applications, polyethylene offers sufficient strength and excellent chemical resistance. It’s often used in applications where impact absorption and flexibility are needed.
Advantages:
Lightweight and flexible
Good resistance to corrosion and chemicals
Low manufacturing cost
Limitations:
Lower mechanical strength
Not suitable for high-speed or high-load conditions
4. Polypropylene (PP)
Why it’s used:
Polypropylene is used in pulleys where weight reduction and chemical resistance are more critical than mechanical strength. It’s common in consumer goods and light mechanical systems.
Advantages:
High chemical and moisture resistance
Lightweight
Affordable and easy to mold
Limitations:
Lower wear resistance compared to PA and POM
Not ideal for high-temperature environments
5. Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Why it’s used:
TPU is selected for applications requiring flexibility, impact resistance, and quiet operation. It’s often used in pulleys where reduced vibration and shock absorption are key.
Advantages:
High elasticity and flexibility
Excellent impact and abrasion resistance
Quiet operation and low noise
Limitations:
Can be more expensive than other thermoplastics
Limited thermal resistance
Choosing the Right Plastic Material
The selection of plastic for bearing pulleys depends on several key factors:
Load capacity: Higher load applications require stronger materials like nylon or acetal.
Speed and friction: Low-friction materials such as POM reduce wear at high speeds.
Environmental conditions: Exposure to moisture, chemicals, or UV may favor polypropylene or polyethylene.
Temperature resistance: For higher temperatures, nylon generally outperforms others.
Cost and availability: Commodity plastics like PE and PP are used when budget is a constraint.
Plastic bearing pulleys offer a balance of performance, cost-efficiency, and versatility, largely driven by the type of plastic material used. Whether it's the high strength of nylon, the stability of acetal, or the flexibility of TPU, each material brings distinct advantages to the table. Understanding the properties of these plastics allows engineers and designers to select the most appropriate option for their specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and durability.





 English
English  Español
Español  日本語
日本語 









