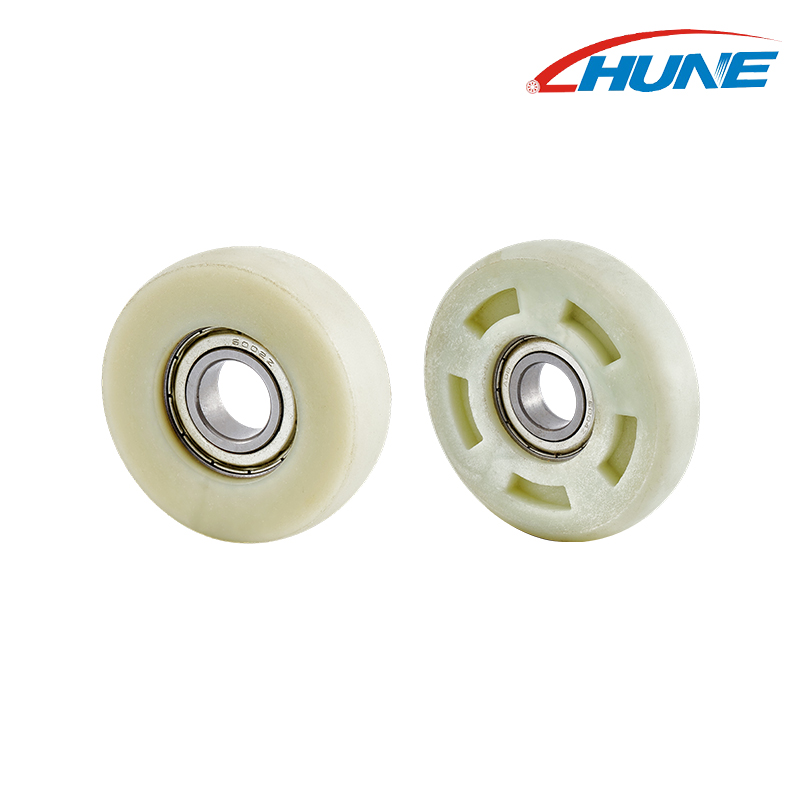
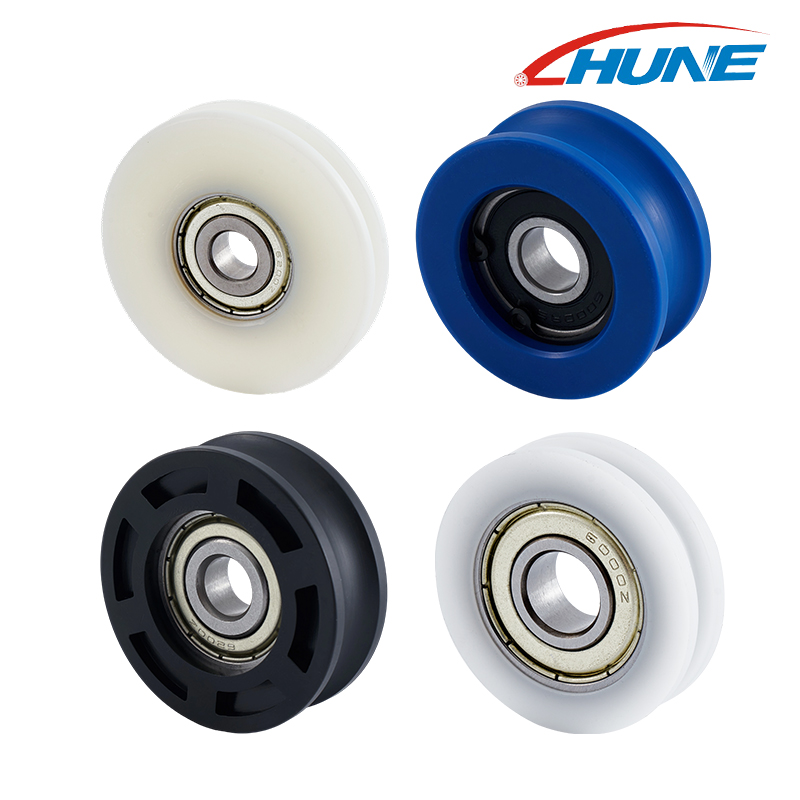
Garage door rollers are not a one-size-fits-all component, and the choice between standard and deep-groove variants often determines how well the roller adapts to your garage door's track and weight. Standard rollers, with their classic design, have long been a go-to for many basic garage door setups, while deep-groove rollers are engineered to address specific challenges like track stability or heavy-door loads. These two types may share the same core purpose, but their unique features make them suited for distinct use cases—so what specific distinctions set them apart and help you determine which is better for your garage door?
Understanding Standard Rollers
1. Structural Features
Standard garage door rollers are designed with a shallow groove profile that keeps the wheel securely in standard residential tracks. Key components include:
- Wheel Material: Typically nylon, reinforced plastic, or light-duty metal alloys, chosen for quiet operation and moderate durability.
- Bearings: Single or double ball bearings ensure smooth rotation and reduce friction. Sealed bearings extend lifespan by preventing dust and moisture intrusion.
- Wheel Diameter and Groove Depth: Optimized for residential door loads, providing sufficient stability without over-engineering.
2. Typical Applications
Standard rollers are best suited for:
- Residential garage doors of moderate size and weight
- Light-duty doors that are used intermittently throughout the day
- Environments with controlled conditions, such as indoor or sheltered garages
- These rollers maintain smooth, consistent operation in low-to-moderate stress scenarios, protecting both the door and the opener from unnecessary strain.
3. Advantages
- Quiet Operation: Nylon or plastic wheels absorb vibrations and reduce noise.
- Affordability: Lower cost makes them easy to replace when necessary.
- Ease of Installation: Compatible with most residential track systems, requiring minimal adjustments.
4. Limitations
- Load Restrictions: Less effective for heavy, oversized, or insulated doors.
- Wear Under High-Frequency Use: Frequent operation can accelerate bearing or wheel degradation.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Dust, debris, or moisture can reduce lifespan if not properly maintained.
Understanding Deep-Groove Rollers
Design and Structure
Deep-groove garage door rollers are engineered with a deeper wheel groove compared to standard rollers, which allows for more secure engagement with the track. These rollers are typically made from reinforced materials, such as high-strength nylon, steel, or engineered composites, to handle heavier loads and reduce deformation under stress. Bearing options include sealed precision ball bearings, which improve rotational efficiency, minimize friction, and extend service life even under high-frequency usage. The combination of groove depth, reinforced materials, and high-quality bearings ensures superior stability and reliability, especially for demanding applications.
Suitable Applications
Deep-groove rollers are ideal for:
- Heavy garage doors, including insulated, wooden, or steel-reinforced models
- Commercial or industrial doors that experience frequent operation
- High-traffic environments where durability and long-term reliability are critical
Their design supports consistent alignment with tracks, reduces vibration and noise, and can accommodate doors that would place too much stress on standard rollers.
Advantages and Limitations
- Advantages:
- Enhanced Stability: Deeper groove and reinforced construction prevent misalignment and wobbling
- Higher Load Capacity: Can support heavy doors without premature wear
- Longer Lifespan: Sealed bearings and durable materials extend service life under frequent use
- Limitations:
- Higher Cost: More expensive than standard rollers due to materials and construction
- Potential Over-Engineering for Light Doors: May not be necessary for small or low-usage residential doors
Comparison of Standard vs. Deep-Groove Garage Door Rollers
|
Roller Type |
Design & Structure |
Suitable Applications |
Advantages |
Limitations |
|
Standard Rollers |
Shallow groove, nylon/plastic/metal, single/double bearings, optimized for residential loads |
Residential doors, light-duty, moderate usage, controlled environments |
Quiet, affordable, easy installation |
Limited load capacity, faster wear under frequent use, sensitive to dust/moisture |
|
Deep-Groove Rollers |
Deeper groove, reinforced nylon/steel/composite, sealed precision bearings, high load support |
Heavy doors, commercial/industrial, high-frequency use |
Enhanced stability, higher load capacity, longer lifespan |
Higher cost, may be over-engineered for light residential doors |
Key Differences Between Standard and Deep-Groove Rollers
1. Groove Depth and Wheel Profile
The groove depth and wheel profile are among the most critical factors in determining the suitability of a roller for different garage door systems. These design features directly affect the roller's ability to stay securely in place and distribute the load evenly along the track.
Standard Rollers:
- Groove Depth: Standard rollers feature a shallow groove profile, which is sufficient for light to moderate door weights.
- Wheel Profile: These rollers generally have a narrower wheel, optimized for typical residential tracks and doors.
Implications: While this design allows for smooth operation, it limits the roller's ability to support heavy or large doors. Over time, the shallow groove may lead to misalignment and excessive wear, especially under continuous or heavy use.
Deep-Groove Rollers:
- Groove Depth: Deep-groove rollers feature a much deeper groove, which ensures more secure and consistent engagement with the track.
- Wheel Profile: The wheel in deep-groove rollers is wider and more robust, designed for heavier loads and industrial-grade use.
- Implications: The deeper groove allows for better load distribution, preventing misalignment and slippage. This makes deep-groove rollers ideal for heavy-duty doors and commercial applications where the door experiences frequent or high-stress use.
2. Load-Bearing Capacity and Material Strength
The load-bearing capacity of a roller determines its ability to carry the weight of the door without degrading performance over time. Material strength is equally important, as it directly affects the durability and service life of the roller.
Standard Rollers:
- Materials: Standard rollers are commonly made from nylon, plastic, or light-duty metal alloys, which offer an optimal balance between cost-effectiveness and moderate durability.
- Load Capacity: These rollers are designed to handle medium-weight residential doors, such as single-car doors or lightweight steel doors.
- Limitations: While affordable, standard rollers are not suitable for heavy doors, such as double-car steel doors, insulated doors, or high-traffic commercial doors. Overloading these rollers will lead to faster wear and premature failure, resulting in costly repairs and downtime.
Deep-Groove Rollers:
- Materials: Deep-groove rollers are typically constructed from high-strength nylon, reinforced steel, or composite materials, making them more durable and capable of supporting much heavier doors.
- Load Capacity: These rollers can handle heavier loads, often supporting insulated, double-car, or industrial-grade doors. The reinforced construction allows them to bear the weight of large, heavy doors without significant deformation or wear.
- Advantages: Deep-groove rollers provide extended service life, even in environments where heavy usage and high door weights are prevalent. This makes them ideal for commercial and industrial applications.
3. Noise Level and Operational Smoothness
The noise level and smoothness of operation are crucial for ensuring that a garage door operates efficiently and quietly. In residential settings, quiet operation is often a top priority, while commercial environments may prioritize durability and performance.
Standard Rollers:
- Noise Level: Standard rollers, especially those with nylon or plastic wheels, tend to provide a relatively quiet operation, making them ideal for residential environments.
- Operational Smoothness: While these rollers operate smoothly under normal conditions, they can become noisy and rough as they wear. Friction and bearing issues can cause squeaking, grinding, or rattling noises, particularly in high-use doors.
- Ideal for: Standard rollers are best for low-to-moderate usage, where quiet operation is desired, and noise is not a primary concern.
Deep-Groove Rollers:
- Noise Level: Deep-groove rollers, thanks to their sealed precision bearings and reinforced construction, tend to provide exceptionally smooth and quiet operation, even under heavy loads and high-frequency usage.
- Operational Smoothness: The reduced friction and high-quality bearings minimize noise and ensure that the door moves smoothly across the track without disruptions.
- Ideal for: Deep-groove rollers are suitable for commercial environments and high-traffic applications, where smooth and quiet operation is critical for operational efficiency.
4. Track Compatibility and Alignment Tolerance
Track compatibility and alignment tolerance are essential factors that influence how effectively the rollers function in maintaining smooth and reliable garage door operation. Misaligned tracks and rollers can lead to door malfunction, increased wear, and even safety hazards.
Standard Rollers:
- Track Compatibility: Standard rollers are designed to work with residential-grade tracks, which are typically narrower and less robust compared to commercial tracks.
- Alignment Tolerance: Standard rollers have limited tolerance for misalignment, which means that any track irregularities or slight misalignment will result in poor door movement. This can lead to additional stress on the opener and other components.
- Implications: While they function well in standard residential setups, standard rollers may fail to maintain proper alignment and stability under heavy-duty or high-traffic conditions.
Deep-Groove Rollers:
- Track Compatibility: Deep-groove rollers are designed to work with heavier, commercial-grade tracks, providing a more secure fit and smoother operation, even in challenging environments.
- Alignment Tolerance: The deeper groove and reinforced construction of deep-groove rollers allow for higher tolerance for misalignment, ensuring that the rollers stay securely seated in the track, even if slight alignment issues occur.
- Implications: These rollers are ideal for commercial, industrial, or heavy-duty garage doors, where misalignment and irregularities are more common and can negatively affect performance.
Comparing Standard vs Deep-Groove Rollers: Key Features and Benefits
|
Feature |
Standard Rollers |
Deep-Groove Rollers |
|
Groove Depth & Wheel |
Shallow groove, narrow wheel, residential use. |
Deep groove, wide wheel, heavy-duty use. |
|
Load-Bearing & Materials |
Nylon/plastic, for medium-weight doors. |
Reinforced steel, for heavy doors. |
|
Noise & Smoothness |
Quiet, but noisy with wear. |
Quiet, smooth even under heavy loads. |
|
Track Compatibility |
Residential tracks, limited alignment tolerance. |
Commercial tracks, better alignment tolerance. |
How to Choose the Right Roller for Your Garage Door
Factors to Consider
- Door Weight: The weight of your garage door is the most important factor in choosing the right roller. Heavier doors require stronger, more durable rollers to prevent premature wear and ensure proper operation.
- Frequency of Use: If your garage door is used frequently, whether for residential or commercial purposes, you'll need rollers designed for high-frequency use. For example, heavy-duty rollers with sealed bearings are ideal for high-traffic doors.
- Environment: The environment in which your garage door operates also matters. In areas with harsh weather conditions or where the door is exposed to dust, moisture, or temperature extremes, it's crucial to choose rollers made from rust-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or reinforced nylon.
- Track Type: Rollers must be compatible with your door's track system. Residential doors typically use smaller tracks, while commercial doors require larger, more robust tracks. Ensure the roller size and groove depth match the track specifications for optimal performance.
Material and Bearing Selection
- Materials: Rollers come in various materials, including nylon, steel, and plastic. Nylon rollers are ideal for residential use due to their smooth operation and low noise. Steel rollers, on the other hand, offer superior strength for heavier, industrial-grade doors.
- Bearings: Rollers with sealed bearings offer better protection from dirt and moisture, extending the lifespan of the roller. Unsealed bearings may be less expensive but can wear out more quickly, especially in environments with heavy exposure to the elements.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper maintenance is essential to extend the life of your garage door rollers and maintain smooth operation.
- Lubrication: Regular lubrication of the rollers and tracks helps reduce friction and prevent wear. Use a high-quality lubricant designed for garage door components to ensure smooth, quiet operation.
- Track Cleaning: Keep the tracks clean and free from debris, dust, and dirt. Regularly inspect the tracks for any obstructions that could cause misalignment or impede the smooth movement of the rollers.
- Alignment Checks: Ensure that the rollers are properly aligned with the tracks. Misalignment can lead to excessive wear, noisy operation, and even premature roller failure.
Signs Rollers Need Replacement
To keep your garage door operating smoothly, it's important to recognize the signs that indicate roller replacement is necessary:
- Excessive Noise: If your garage door starts making squeaking, grinding, or rattling noises during operation, it may be a sign that the rollers are worn or damaged.
- Door Misalignment: If the door becomes misaligned, doesn't close properly, or struggles to open smoothly, it's time to check the rollers for wear or damage.
- Sluggish Movement: If your garage door becomes slow or sluggish to open or close, it may be due to worn rollers that need replacing to maintain optimal performance.
Choosing high-quality rollers is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of your garage door. Hune offers a wide range of rollers designed to meet various needs, from residential doors to heavy-duty commercial applications. With our extensive selection, you're sure to find the perfect roller that fits your specific requirements.





 English
English  Español
Español  日本語
日本語 









